Understanding Alligation or Mixture Formulae With Examples
In this class, We discuss Understanding Alligation or Mixture Formulae With Examples.
The reader should have prior knowledge of ratios and profit and loss. Click Here.
Alligation:
The rule enables us to find the ratio in which two or more ingredients at a given price must be mixed to produce a mixture at the desired Price.
Example:
In what ratio must rice at 930 per KG be mixed with rice at 1080 per KG?
The mixture is worth Rs 1000 per KG.
Solution:
First, we understand how the example is solved using percentages.
(x% of 930) + ((100 – x)% of 1080) = 1000.
(x/100) * 930 + ((100 – x)/100) * 1080 = 1000
15x = 800
x = 53.33
100 – x = 46.66
The first rice should be 53.33 percent, and the second should be 46.66 percent in one KG.
The below diagram shows the way we use the alligation rule.
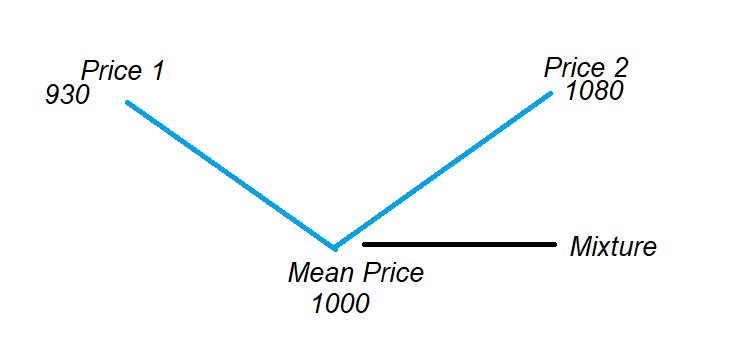
Mean Price: the mean Price is the mixture price.
Rule of Alligation:
If two ingredients are mixed, then the ratio to obtain the mean price = Quantity of Cheaper/ Quantity of costly
Quantity of Cheaper/ Quantity of costly = (CP of costly – mean Price) / (Mean price – CP of cheaper)
The below diagram shows the rule of alligation.
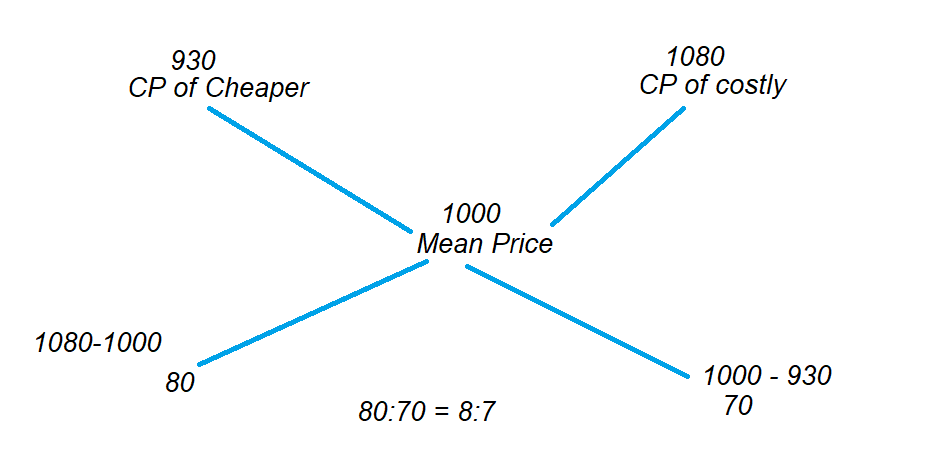
The ratio is 8: 7
Ratio converted to percentage
8/15 * 100 = 53.33
7/15 * 100 = 46.66
