Protocol Source IP and Destination IP Fields in IPv4
For Complete YouTube Video: Click Here
We will try to understand Protocol Source IP and Destination IP Fields in IPv4 in this class.
We have already discussed the concepts of header checksum in our previous class.
Protocol Source IP and Destination IP Fields in IPv4
The image below is the IPv4 Header.
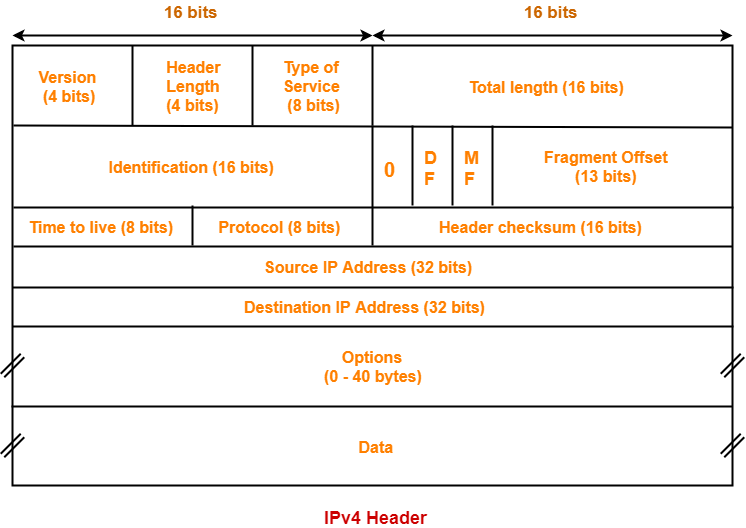
The Protocol field in the IPv4 header contains a number indicating the type of data found in the payload portion of the datagram.
So far, we have discussed that data will get transmitted in the packet’s payload.
But many different messages are transmitted in the data packet.
For example, ICMP messages are transmitted for sending the error messages.
The transport layer protocols like TCP and UDP are transmitted.
The list of all protocol numbers is provided in the table below.
All these numbers are maintained by IANA [Internet Assigned Numbers Authourity].
| Hex | Protocol Number | Keyword | Protocol |
| 0x00 | 0 | HOPOPT | IPv6 Hop-by-Hop Option |
| 0x01 | 1 | ICMP | Internet Control Message Protocol |
| 0x02 | 2 | IGMP | Internet Group Management Protocol |
| 0x03 | 3 | GGP | Gateway-to-Gateway Protocol |
| 0x04 | 4 | IP-in-IP | IP in IP (encapsulation) |
| 0x05 | 5 | ST | Internet Stream Protocol |
| 0x06 | 6 | TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| 0x07 | 7 | CBT | Core-based trees |
| 0x08 | 8 | EGP | Exterior Gateway Protocol |
| 0x09 | 9 | IGP | Interior Gateway Protocol (any private interior gateway, for example Cisco’s IGRP) |
| 0x0A | 10 | BBN-RCC-MON | BBN RCC Monitoring |
| 0x0B | 11 | NVP-II | Network Voice Protocol |
| 0x0C | 12 | PUP | Xerox PUP |
| 0x0D | 13 | ARGUS | ARGUS |
| 0x0E | 14 | EMCON | EMCON |
| 0x0F | 15 | XNET | Cross Net Debugger |
| 0x10 | 16 | CHAOS | Chaos |
| 0x11 | 17 | UDP | User Datagram Protocol |
| 0x12 | 18 | MUX | Multiplexing |
| 0x13 | 19 | DCN-MEAS | DCN Measurement Subsystems |
| 0x14 | 20 | HMP | Host Monitoring Protocol |
| 0x15 | 21 | PRM | Packet Radio Measurement |
| 0x16 | 22 | XNS-IDP | XEROX NS IDP |
| 0x17 | 23 | TRUNK-1 | Trunk-1 |
| 0x18 | 24 | TRUNK-2 | Trunk-2 |
| 0x19 | 25 | LEAF-1 | Leaf-1 |
| 0x1A | 26 | LEAF-2 | Leaf-2 |
| 0x1B | 27 | RDP | Reliable Data Protocol |
| 0x1C | 28 | IRTP | Internet Reliable Transaction Protocol |
| 0x1D | 29 | ISO-TP4 | ISO Transport Protocol Class 4 |
| 0x1E | 30 | NETBLT | Bulk Data Transfer Protocol |
| 0x1F | 31 | MFE-NSP | MFE Network Services Protocol |
| 0x20 | 32 | MERIT-INP | MERIT Internodal Protocol |
| 0x21 | 33 | DCCP | Datagram Congestion Control Protocol |
| 0x22 | 34 | 3PC | Third Party Connect Protocol |
| 0x23 | 35 | IDPR | Inter-Domain Policy Routing Protocol |
| 0x24 | 36 | XTP | Xpress Transport Protocol |
| 0x25 | 37 | DDP | Datagram Delivery Protocol |
| 0x26 | 38 | IDPR-CMTP | IDPR Control Message Transport Protocol |
| 0x27 | 39 | TP++ | TP++ Transport Protocol |
| 0x28 | 40 | IL | IL Transport Protocol |
| 0x29 | 41 | IPv6 | IPv6 Encapsulation (6to4 and 6in4) |
| 0x2A | 42 | SDRP | Source Demand Routing Protocol |
| 0x2B | 43 | IPv6-Route | Routing Header for IPv6 |
| 0x2C | 44 | IPv6-Frag | Fragment Header for IPv6 |
| 0x2D | 45 | IDRP | Inter-Domain Routing Protocol |
| 0x2E | 46 | RSVP | Resource Reservation Protocol |
| 0x2F | 47 | GRE | Generic Routing Encapsulation |
| 0x30 | 48 | DSR | Dynamic Source Routing Protocol |
| 0x31 | 49 | BNA | Burroughs Network Architecture |
| 0x32 | 50 | ESP | Encapsulating Security Payload |
| 0x33 | 51 | AH | Authentication Header |
| 0x34 | 52 | I-NLSP | Integrated Net Layer Security Protocol |
| 0x35 | 53 | SwIPe | SwIPe |
| 0x36 | 54 | NARP | NBMA Address Resolution Protocol |
| 0x37 | 55 | MOBILE | IP Mobility (Min Encap) |
| 0x38 | 56 | TLSP | Transport Layer Security Protocol (using Kryptonet key management) |
| 0x39 | 57 | SKIP | Simple Key-Management for Internet Protocol |
| 0x3A | 58 | IPv6-ICMP | ICMP for IPv6 |
| 0x3B | 59 | IPv6-NoNxt | No Next Header for IPv6 |
| 0x3C | 60 | IPv6-Opts | Destination Options for IPv6 |
| 0x3D | 61 | Any host internal protocol | |
| 0x3E | 62 | CFTP | CFTP |
| 0x3F | 63 | Any local network | |
| 0x40 | 64 | SAT-EXPAK | SATNET and Backroom EXPAK |
| 0x41 | 65 | KRYPTOLAN | Kryptolan |
| 0x42 | 66 | RVD | MIT Remote Virtual Disk Protocol |
| 0x43 | 67 | IPPC | Internet Pluribus Packet Core |
| 0x44 | 68 | Any distributed file system | |
| 0x45 | 69 | SAT-MON | SATNET Monitoring |
| 0x46 | 70 | VISA | VISA Protocol |
| 0x47 | 71 | IPCU | Internet Packet Core Utility |
| 0x48 | 72 | CPNX | Computer Protocol Network Executive |
| 0x49 | 73 | CPHB | Computer Protocol Heart Beat |
| 0x4A | 74 | WSN | Wang Span Network |
| 0x4B | 75 | PVP | Packet Video Protocol |
| 0x4C | 76 | BR-SAT-MON | Backroom SATNET Monitoring |
| 0x4D | 77 | SUN-ND | SUN ND PROTOCOL-Temporary |
| 0x4E | 78 | WB-MON | WIDEBAND Monitoring |
| 0x4F | 79 | WB-EXPAK | WIDEBAND EXPAK |
| 0x50 | 80 | ISO-IP | International Organization for Standardization Internet Protocol |
| 0x51 | 81 | VMTP | Versatile Message Transaction Protocol |
| 0x52 | 82 | SECURE-VMTP | Secure Versatile Message Transaction Protocol |
| 0x53 | 83 | VINES | VINES |
| 0x54 | 84 | TTP | TTP |
| 0x54 | 84 | IPTM | Internet Protocol Traffic Manager |
| 0x55 | 85 | NSFNET-IGP | NSFNET-IGP |
| 0x56 | 86 | DGP | Dissimilar Gateway Protocol |
| 0x57 | 87 | TCF | TCF |
| 0x58 | 88 | EIGRP | EIGRP |
| 0x59 | 89 | OSPF | Open Shortest Path First |
| 0x5A | 90 | Sprite-RPC | Sprite RPC Protocol |
| 0x5B | 91 | LARP | Locus Address Resolution Protocol |
| 0x5C | 92 | MTP | Multicast Transport Protocol |
| 0x5D | 93 | AX.25 | AX.25 |
| 0x5E | 94 | OS | KA9Q NOS compatible IP over IP tunneling |
| 0x5F | 95 | MICP | Mobile Internetworking Control Protocol |
| 0x60 | 96 | SCC-SP | Semaphore Communications Sec. Pro |
| 0x61 | 97 | ETHERIP | Ethernet-within-IP Encapsulation |
| 0x62 | 98 | ENCAP | Encapsulation Header |
| 0x63 | 99 | Any private encryption scheme | |
| 0x64 | 100 | GMTP | GMTP |
| 0x65 | 101 | IFMP | Ipsilon Flow Management Protocol |
| 0x66 | 102 | PNNI | PNNI over IP |
| 0x67 | 103 | PIM | Protocol Independent Multicast |
| 0x68 | 104 | ARIS | IBM’s ARIS (Aggregate Route IP Switching) Protocol |
| 0x69 | 105 | SCPS | SCPS (Space Communications Protocol Standards) |
| 0x6A | 106 | QNX | QNX |
| 0x6B | 107 | A/N | Active Networks |
| 0x6C | 108 | IPComp | IP Payload Compression Protocol |
| 0x6D | 109 | SNP | Sitara Networks Protocol |
| 0x6E | 110 | Compaq-Peer | Compaq Peer Protocol |
| 0x6F | 111 | IPX-in-IP | IPX in IP |
| 0x70 | 112 | VRRP | Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol, Common Address Redundancy Protocol (not IANA assigned) |
| 0x71 | 113 | PGM | PGM Reliable Transport Protocol |
| 0x72 | 114 | Any 0-hop protocol | |
| 0x73 | 115 | L2TP | Layer Two Tunneling Protocol Version 3 |
| 0x74 | 116 | DDX | D-II Data Exchange (DDX) |
| 0x75 | 117 | IATP | Interactive Agent Transfer Protocol |
| 0x76 | 118 | STP | Schedule Transfer Protocol |
| 0x77 | 119 | SRP | SpectraLink Radio Protocol |
| 0x78 | 120 | UTI | Universal Transport Interface Protocol |
| 0x79 | 121 | SMP | Simple Message Protocol |
| 0x7A | 122 | SM | Simple Multicast Protocol |
| 0x7B | 123 | PTP | Performance Transparency Protocol |
| 0x7C | 124 | IS-IS over IPv4 | Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS) Protocol over IPv4 |
| 0x7D | 125 | FIRE | Flexible Intra-AS Routing Environment |
| 0x7E | 126 | CRTP | Combat Radio Transport Protocol |
| 0x7F | 127 | CRUDP | Combat Radio User Datagram |
| 0x80 | 128 | SSCOPMCE | Service-Specific Connection-Oriented Protocol in a Multilink and Connectionless Environment |
| 0x81 | 129 | IPLT | |
| 0x82 | 130 | SPS | Secure Packet Shield |
| 0x83 | 131 | PIPE | Private IP Encapsulation within IP |
| 0x84 | 132 | SCTP | Stream Control Transmission Protocol |
| 0x85 | 133 | FC | Fibre Channel |
| 0x86 | 134 | RSVP-E2E-IGNORE | Reservation Protocol (RSVP) End-to-End Ignore |
| 0x87 | 135 | Mobility Header | Mobility Extension Header for IPv6 |
| 0x88 | 136 | UDPLite | Lightweight User Datagram Protocol |
| 0x89 | 137 | MPLS-in-IP | Multiprotocol Label Switching Encapsulated in IP |
| 0x8A | 138 | manet | MANET Protocols |
| 0x8B | 139 | HIP | Host Identity Protocol |
| 0x8C | 140 | Shim6 | Site Multihoming by IPv6 Intermediation |
| 0x8D | 141 | WESP | Wrapped Encapsulating Security Payload |
| 0x8E | 142 | ROHC | Robust Header Compression |
| 0x8F | 143 | Ethernet | IPv6 Segment Routing (TEMPORARY – registered 2020-01-31, expired 2021-01-31) |
| 0x90-0xFC | 144-252 | Unassigned | |
| 0xFD-0xFE | 253-254 | Use for experimentation and testing | |
| 0xFF | 255 | Reserved |
The other two fields of the IPv4 header are Source IP and Destination IP field.
The source IP is the IP address of the sending system, and the destination IP is the address of receiving system.
You can find the detailed discussion on IP addresses here.
This is all about Protocol Source IP and Destination IP Fields in IPv4.
