What is Address Resolution Protocol ARP
For Complete YouTube Video: Click Here
This class will try to understand What is Address Resolution Protocol ARP.
The ARP full form is Address Resolution Protocol.
We have already discussed the concepts of Internet Protocol and the difference between RIP and OSPF in our previous classes.
What is Address Resolution Protocol ARP
Address Resolution Protocol ARP is a network layer protocol to get the MAC address of the given IP address.
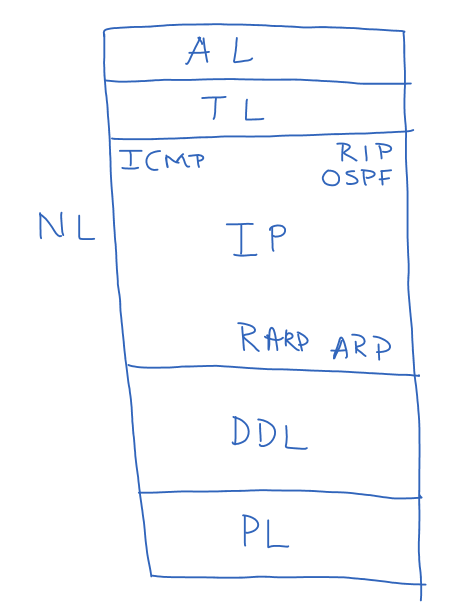
The image below shows how the protocols are arranged in the network layer.
As shown below, we will consider the sample network to understand this concept.
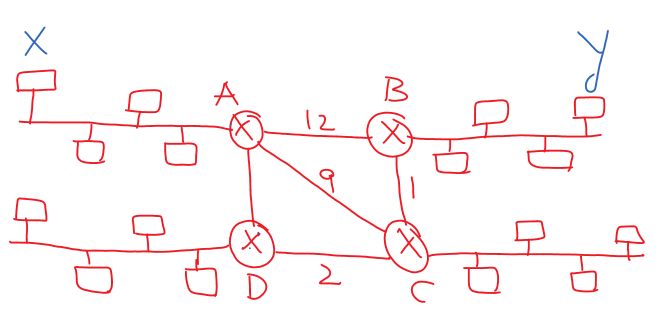
The above image assumes that system X wants to communicate with system Y.
The X will add the transport layer header, network layer header, and the data link layer head and the tail for that communication to happen.
As we have discussed, the data link layer is a node-to-node communication, and the node to which the data has to be transmitted is router A.
For that node-to-node communication, the data link layer of X should have the MAC address of router A.
Node X will have the IP address of A as the default router address in the IP settings.
As the network layer protocols are unaware of the MAC addresses, the ARP Address Resolution Protocol will come into action.
The IP will now request the ARP to get the MAC address of A.
The ARP will broadcast the ARP request packet into the network, stating that I have the IP address of A and want the MAC address.
As the request packet is received at A, it will send the MAC address in response.
This MAC address is used in the header field of the data link layer as the destination MAC address.
Using the same procedure, router A based on the routing table, the data must be transmitted from router A to router D to router C to router B.
As the destination node is directly connected to router B, the router has to get the MAC address of node Y.
In the same procedure of calling the Address Resolution Protocol, node B will get Y’s MAC address, and the data will reach the destination.
