Split Horizon A Solution to Count to Infinity Problem
For Complete YouTube Video: Click Here
We will try to understand Split Horizon A Solution to Count to Infinity Problem in this class.
We have already discussed the concept of Routing Loops and the Count to Infinity Problem in our previous classes.
Split Horizon A Solution to Count to Infinity Problem
To understand this concept, we will consider the example from our previous class.
The image below shows the distance vectors after stabilization.
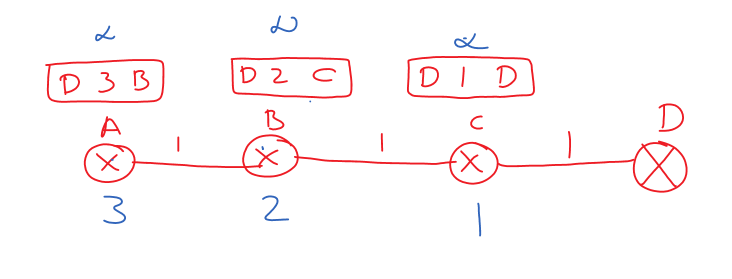
Assume that the node C and D link has been broken.
In our previous class, we have seen that the rouging loops occur from here, and it will lead to the count infinity problem.
In split-horizon, the nodes will share Infinity if there is a dependence on the immediate node for it to transfer to the destination.
Consider the image below where the routers exchanged distance vectors in the first round to understand better.
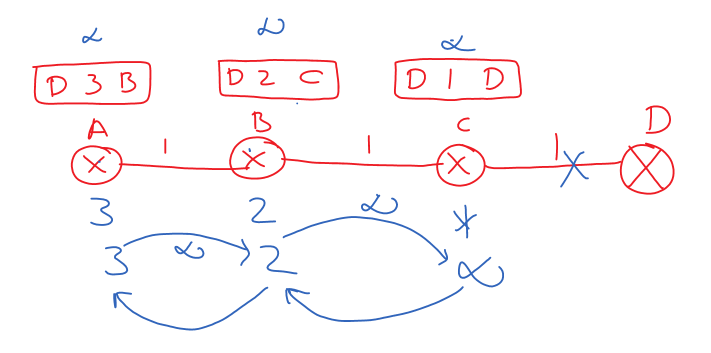
Consider the distance vector transfer from B to C in the above image.
The B is transmitting Infinity instead of two because for B to transmit the data to D. It is dependent on C.
Similarly, the distance vector transfer between A to B is also Infinity because for A to transmit the data to D, it is dependent on B.
In the second round of exchange the distance vector at A is updated to infinity as shown below.
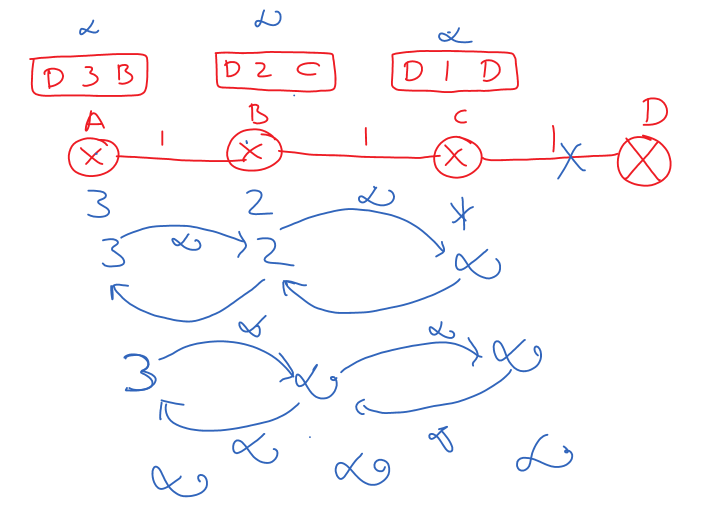
In this way, the infinity value will get updated on all the routers.
