C Programming Practice 2 on Ternary Operator
For Complete YouTube Video: Click Here
In this class, we will do C Programming Practice 2 on Ternary Operator.
We have covered Arithmetic, Assignment, Increment-Decrement, Bitwise, Shift, Ternary, Relational, and Logical Operators.
Here we will solve some C Programming Practice on Ternary Operators.
C Programming Practice on Ternary Operators
The example below is a program on Ternary Operators.
int a = 2, b = 3, c = 4, l;
l = (a>b) ? (a>c ? a : c) : (b>c ? b : c);
In the above program, we have four variables a, b, c, l.
The values assigned to a, b, and c are 2, 3, and 4.
The ternary operators are [?:].
The above program finds a large number among the three variables a, b, and c.
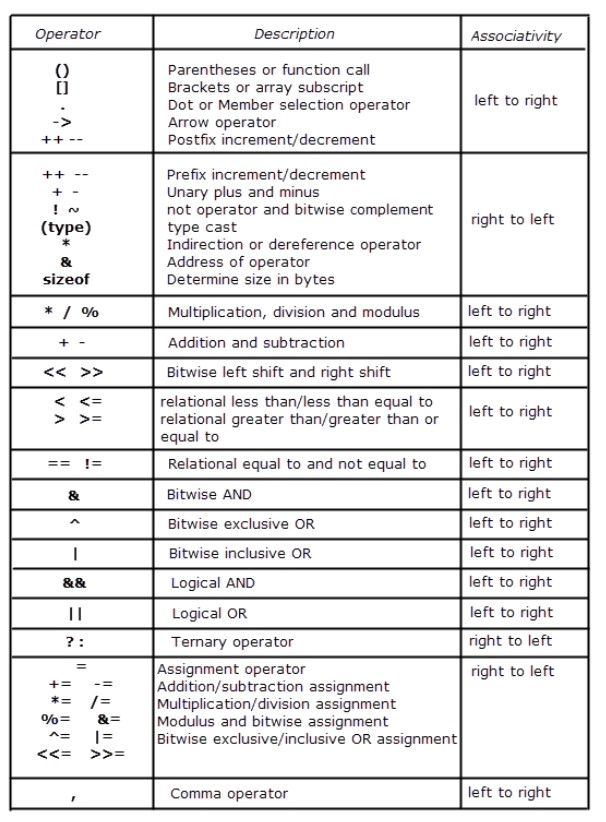
The image below is the operator precedence and associativity table.
The expression uses ternary operator in the program is l = (a>b) ? (a>c ? a : c) : (b>c ? b : c).
The C compiler will execute a>b if it is true in the above expression, then (a>c ? a: c) will be performed.
a>b means among a and b; a is large.
Now a has to be compared with c.
(a>c ? a : c) is a ternary operator.
In the above expression, if a > c, the output will be a.
Else the output will be c.
If a is NOT greater than b, then (b>c ? b: c) will be executed.
If b>c, b is larger else, c is larger.
